Technical Challenge
Prematurely born babies (neonates) are kept in an infant incubator until they can maintain their temperature on their own. The main environmental factor affecting a premature neonate is thermo-neutrality, as the baby is incapable of regulating and maintaining his/her body temperature at a constant level. Significant temperature differences inside an infant incubator therefore may cause hypothermia.
The technical challenge is to optimize infant incubator design in order to minimize internal temperature variations.
Veryst Solution
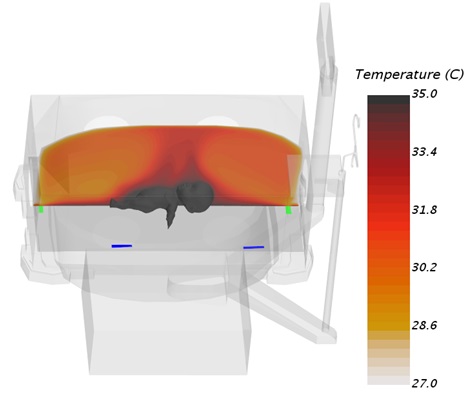
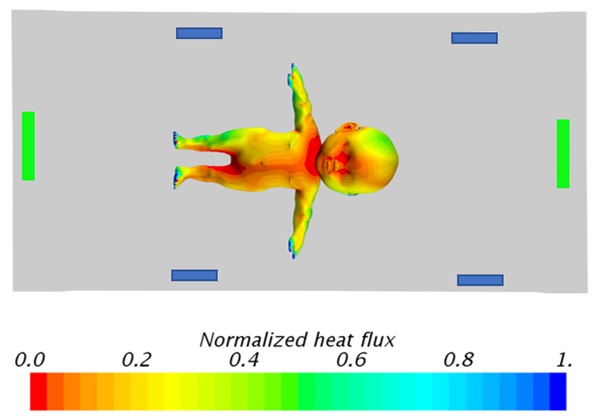
Veryst developed a computational model of heat transfer inside an infant incubator. The model, developed using STAR-CCM+, accounts for conduction and convection. The incubator has four air inlets (highlighted in blue in Figures 1 and 2) with a flow rate of 51 cm³/s, a temperature of 37°C, and two outlets (highlighted in green in Figures 1 and 2).
The figure also shows the geometry of the incubator and steady state temperate distribution along its center plane. Temperature is not uniform inside the incubator, creating a non-uniform heat flux from the body, which is shown in Figure 2.
The model provides valuable insight for improving the design of the incubator to minimize the temperature difference and obtain a more uniform heat flux from the baby’s body.